for expert insights on the most pressing topics financial professionals are facing today.
Learn MoreInherited IRAs are a significant and oftentimes complicated part of many clients’ Estate Plans. As an advisor, it takes diligence to stay aware of the updates made to IRA rules each year so that you can provide clients with the right advice. To help, eMoney is designed to provide you the best possible platform to plan for and illustrate the many different strategies for an inherited IRA.
IRA distribution plans depend on two main factors: The relationship of the beneficiary to the original owner and the age of the original owner when they pass the IRA to the beneficiary. Begin by focusing on the beneficiary’s relationship to the original owner.
When working with a client who has inherited an IRA from a non-spouse and who chooses to take the Required Minimum Distributions (RMDs) over their lifetime, go to the Advanced Facts page and then select the account in question. From there Navigate to the Beneficiaries tab and scroll down to the Required Minimum Distributions section.
Once there you will see an Inherited from a Non-Spouse toggle. Set this to Yes and then click the link to Look Up RMD Factor. This will prompt the system to ask you to enter the year in which the client inherited the IRA, which, in conjunction with the beneficiary’s age, allows our system to calculate the appropriate RMD Factor.
The system automatically calculates the RMDs for the beneficiary using the correct IRS life tables specifically for beneficiaries. There is no need to enter scheduled transfer flows to model the RMDs.
You also have the option to set up a total distribution, which can be modeled with an Other Income flow designated as Ordinary Income for tax purposes in the year the lump sum will be received.
When working with a Surviving Spouse and modeling a future death scenario in the system, there are three common techniques to model:
Total distributions and rollovers can be modeled using a transfer flow from the inherited account to either the core cash, in the case of a distribution or the spouses IRA in the case of a rollover.
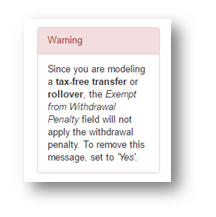
In these instances, the system will recognize and notify you that you are modeling a tax-free transfer or rollover. You can dismiss this message by setting the Exempt from Withdrawal field to Yes manually.
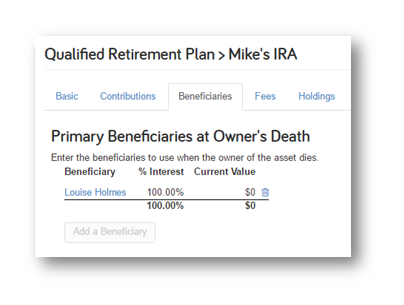
When modeling a Spouse that is simply inheriting an IRA and not withdrawing any funds, set them as the beneficiary and upon the owner’s death the account will automatically recalculate the RMD’s.